Critical raw materials: the case of Feldspar
Analysis of critical raw materials identified by the European Commission
Published by Pasquale Marzano. .
Inorganic Chemicals Critical raw materialsThis article delves into the criticality of feldspar for the European economy, according to the criteria of economic importance[1] and supply risk[2] for European businesses, illustrated in the analysis Critical Raw Materials: the importance of substitutes.
Economic importance of Feldspar
Feldspar represents one of the most widespread groups of minerals on Earth, as it constitutes approximately 60% of the composition of rocks forming the Earth's crust. This group of minerals is defined as an aluminosilicate, a compound derived from aluminum oxide and silicon dioxide, and can contain varying amounts of calcium, potassium, or sodium.
Feldspar has significant economic importance due to its use in the production of ceramics and glass, improving the strength, toughness, and durability of products. In the ceramic production process, feldspar is the second most important raw material after clay. In glass production, it acts as a source of alumina, which provides corrosion resistance, and as a flux, lowering the melting temperature of glass mixtures to make their processing more efficient.
More generally, the sectors using feldspar are divided as follows:
- ceramics: tiles and glazes, 79%;
- ceramics: sanitaryware and tableware, 8%;
- glass, 10%;
- other sectors (paints, rubber, and plastics as filler, extender, or adhesive additive, etc.), 3%.
Globally, production is concentrated in Turkey, India, and China. Despite being considered an abundant raw material, the geographical distribution of feldspar is uneven, which could create supply challenges, especially considering the expected growth in global demand in the coming years.
Regarding substitute goods, there are numerous alternatives to feldspar, but they cannot effectively replace its use. Additionally, the percentage of use that substitute goods can cover does not exceed 5% in the production of tiles and glazes and glass.
Criticality of Feldspar in the EU market
Despite its global availability, feldspar presents several critical issues in the European Union (EU) market, mainly related to import dependency and supply chain vulnerabilities. The EU imports over 60% of its feldspar needs from Turkey, making the European market highly dependent on a single external supplier.
The following chart illustrates the evolution of the share of EU feldspar supplies as a percentage of total annual EU imports (analysis based on ExportPlanning data).
Share of EU Feldspar Supplies
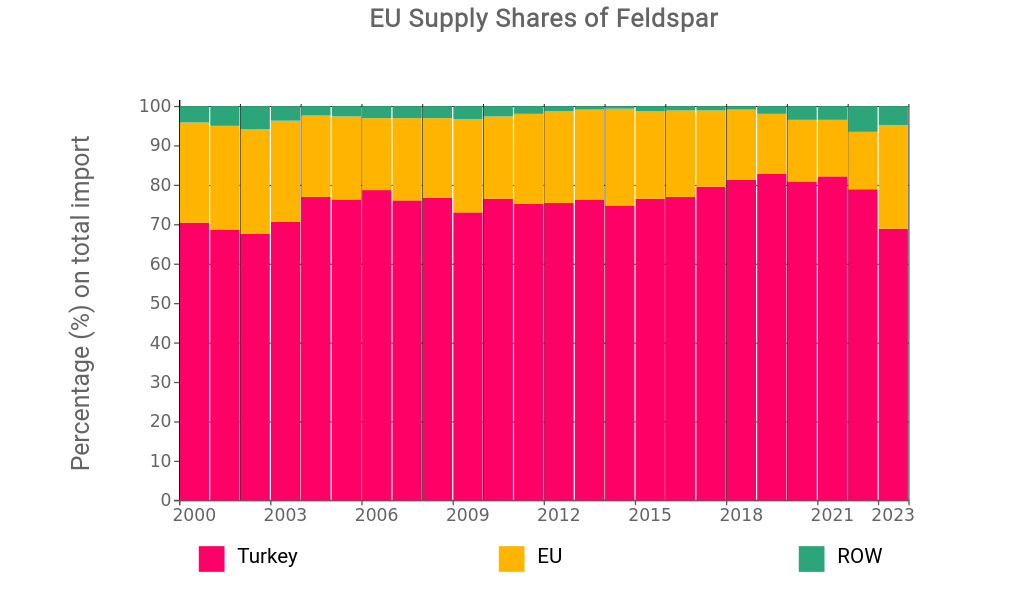
From 2000 to 2023, Turkey has covered an increasing share of European feldspar supplies, exceeding 80% of total EU supplies starting from 2018. In 2023, Turkey's share dropped to 68%, in favor of EU member countries, which grew to 26%.
Among EU suppliers, Italy stands out, producing about 7% of the total feldspar globally.
As for other international EU partners, the shares are not significant and have never historically exceeded 6%.
The price of Feldspar
Given Turkey's importance as the main feldspar supplier to the EU, it is plausible to consider the price of Turkish feldspar as representative of the EU market price.
The following chart shows this price, processed by PricePedia and expressed in euros per ton.
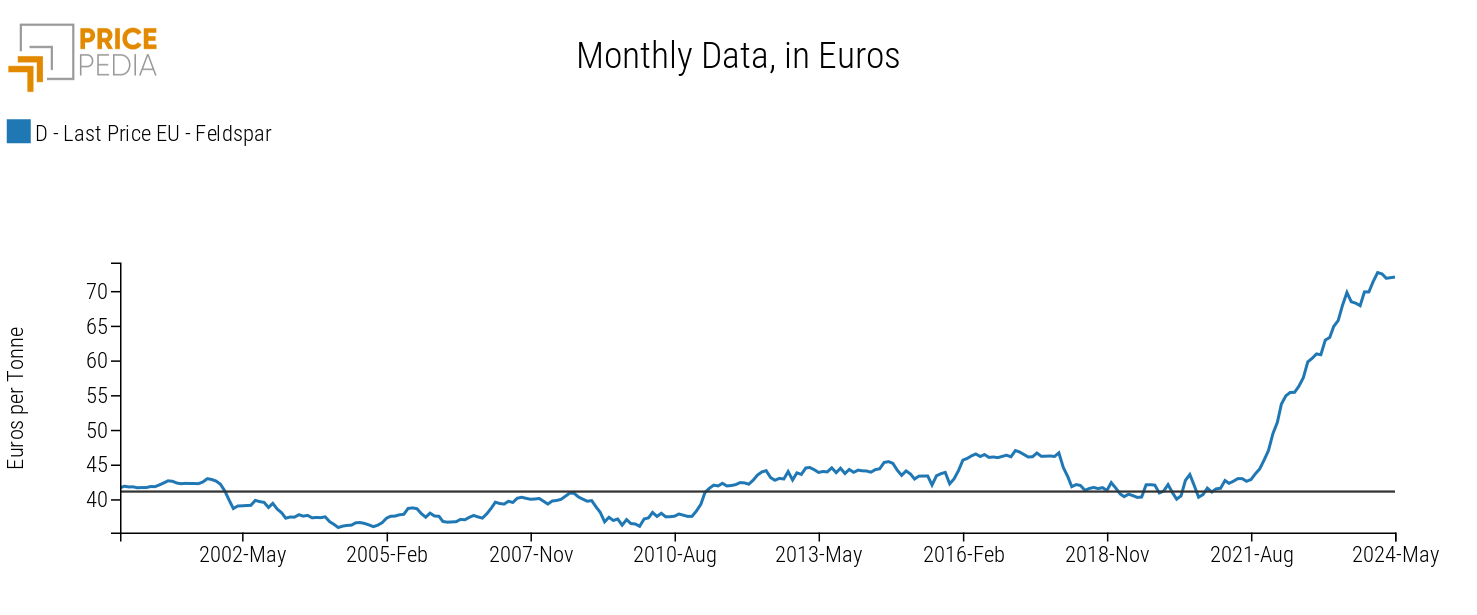
After a long period of stable prices between 35 and 50 euros per ton from 2000 to 2021, in the last two years, the prices of Turkish feldspar have increased rapidly, registering in March 2024 an increase of +76% compared to the 2000-2021 average. In recent months, prices have remained high at historic highs.
Conclusions
The price dynamics of Turkish feldspar exemplify the importance for the EU of having greater diversification of raw material suppliers. In the coming years, it will be important to continue, at the EU level, the efforts started in 2023 to increase the range of suppliers and reduce supply risk.
Do you want to stay up-to-date on commodity market trends?
Sign up for PricePedia newsletter: it's free!
1. The economic importance indicator outlined in the Critical Raw Materials Act defines the importance of a commodity based on the number of applications and the added value generated by the user sectors.
2. The supply risk indicator defined by the Commission reflects the risk of supply disruption of a given commodity and mainly depends on the degree of EU imports, the concentration of imports in a few countries, and the governance of the supplying countries. It is measured both at the extraction phase of the raw material and at the first processing phase.
Pasquale Marzano
Economist and data scientist. At PricePedia he deals with the analysis of commodity markets, forecasting models for raw material prices and management of reference databases.