Price of electrical steel sheets in the spotlight for EU buyers
Compared to the pre-COVID situation, prices of silicon electrical sheets remain particularly high
Published by Luigi Bidoia. .
Electrical Steel Commodity price cycle 2020-2023
One of the commodity prices currently receiving particular attention from procurement departments is that of cold-rolled non-grain oriented (NGO) silicon electrical steel[1].
A few numbers are sufficient to describe the current unique situation in this market. In 2019, the prices for cold-rolled non-magnetic and NGO magnetic coils were respectively 573 and 734 euros per ton, with a premium of 28% for the magnetic steel. In the early months of 2024, these prices were 808 and 1395 euros/ton, with a premium of over 70% for the magnetic steel.
While at the beginning of 2024, the price of non-magnetic cold-rolled steel was 40% higher than in 2019, for magnetic steel the increase was 90%.
Many procurement departments are wondering what factors underlie this difference. This article explains how historically higher prices are now recorded for NGO sheet, but the determinants of these higher prices must be sought in the nearby market of grain-oriented (GO) magnetic sheet.
Current Prices of electrical steel and NGO silicon sheet
The table below shows the prices of non-alloy electrical steel and NGO silicon electrical sheet. The 2024 prices refer to the average of the first three months of the year.
Prices (euro/tonne) of Electrical Steel and Non-Grain Oriented (NGO) Electrical Sheet
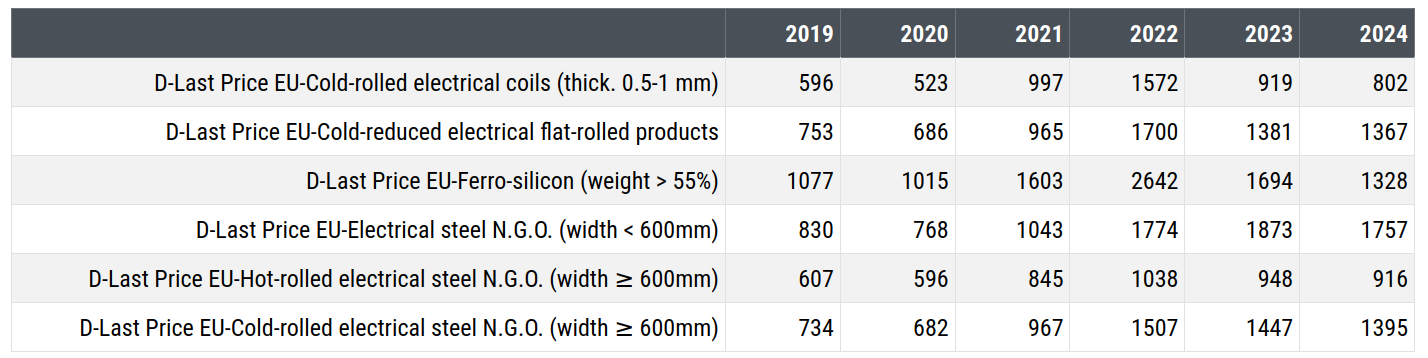
The first two prices listed in the table relate to products made of non-alloy magnetic steel, both cold-rolled, the first with a width exceeding 600 millimeters, the second with a width less. The last three prices in the table, identified by the acronym NGO, are instead sheets made with silicon electrical steel; one of these products is hot-rolled; the other two are cold-rolled; the first of the three has a width less than 600 millimeters; the other two have a greater width.
The table also includes the price of silicon iron, which represents a significant cost component of the three NGO sheets.
From the analysis of the data presented in the table, it is evident that, after peaking in 2022, the prices of the two non-alloy electrical steels have seen a significant reduction. Similarly significant was the reduction in the price of silicon iron, which dropped from 2642 euros per tonne in the average of 2022 to 1328 euros in the first three months of 2024.
Conversely, after peaking in 2022, the three NGO electrical sheets have recorded only weak reductions in the following months, maintaining historically very high prices even in the first months of 2024.
A possible determinant of these high prices can be sought in what happened in the nearby market of grain-oriented (GO) electrical sheets.
Do you want to stay up-to-date on commodity market trends?
Sign up for PricePedia newsletter: it's free!
The Global Market for Grain-Oriented Electrical Sheets
After reaching a peak in the spring of 2023, for nearly a year now, the price in Europe of grain-oriented electrical sheets (G.O) has been undergoing a reduction phase, more pronounced for the sheets in coils (with a width exceeding 600 millimeters); slightly less pronounced for the sheets in strips (with a width less than 600 millimeters). The following chart compares the two prices of G.O sheets with the price of Chinese export of G.O sheets in coils.
Prices worldwide of grain-oriented electrical steel
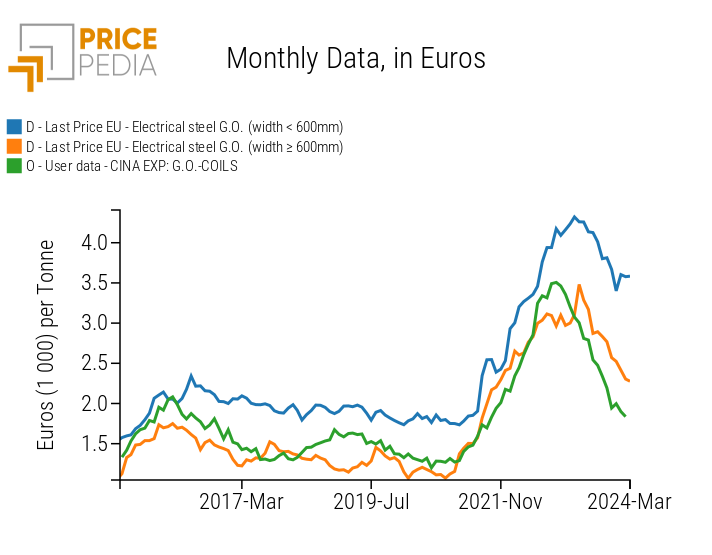
There is no doubt that Chinese export prices anticipated the recent phase of price reduction in Europe. In fact, the price of Chinese exports reached its peak in December 2022, then began a phase of decrease that led to a reduction in Chinese prices by -46% by February 2024, returning to the levels of summer 2021. The phase of price reduction in Europe started in May 2023, accumulating a reduction of -35% by March 2024.
The leading role that Chinese prices have in relation to European prices is justified by the importance of Chinese exports in the global trade of this type of magnetic sheet and by the weight that Chinese flows have on EU imports. In 2023, China indeed exported over 1.3 billion dollars of GO sheet in coils, of which 178 million went to the EU, accounting for 37% of the total EU imports from extra-EU countries.
European Commission Anti-Dumping Measures
Regarding upcoming developments, it is important to note that on January 18, 2022, the European Commission established a customs duty for imports of GO sheet steel from China, Japan, the United States, Russia, and South Korea (COMMISSION IMPLEMENTING REGULATION (EU) 2022/58). The tariffs become effective for import prices below the thresholds of 2043 euros, 1873 euros, and 1536 euros per tonne, respectively for sheets with a maximum loss not exceeding 0.9 W/kg, between 0.9 -1.05 W/kg, and above 1.05 W/kg. The current prices of GO magnetic sheet in coils on the European market are currently well above 2000 euros/ton. Therefore, these duties are not affecting the current market prices in the EU, but they may have influenced the choices of producers by providing relative certainty that the price in the EU market will not fall below 2000 euros/ton.
Subsequently, on June 7, 2023, the European Commission established a definitive anti-dumping duty on imports of certain hot-rolled flat products (COMMISSION IMPLEMENTING REGULATION (EU) 2023/1122). These products include hot-rolled NGO silicon magnetic steels, with a rate varying depending on the manufacturing company.
Given the limited volume of imports from China of this specific product, it is likely that this duty has not had effects on the European market for silicon magnetic steel.
Conclusions
The peculiar case of the prices of magnetic sheets has been the subject of ongoing in-depth analysis by the PricePedia team over the last year. Further insights will likely be necessary.
With the current state of knowledge, the main factor appearing to cause the persistence of historically high prices for NGO magnetic sheets is the high prices reached during the 2021-2021 cycle for GO magnetic sheets and the anti-dumping duties in place on its EU imports from many partner countries, including China and Japan, global leaders in these products.
After the introduction of the anti-dumping duty on EU imports of GO magnetic steel, some producers may have decided to prioritize the production of this type of magnetic steel at the expense of NGO magnetic steel. This shift has limited the supply in the EU of NGO magnetic sheet, supporting its prices even in the recent phase of significant production cost reductions.
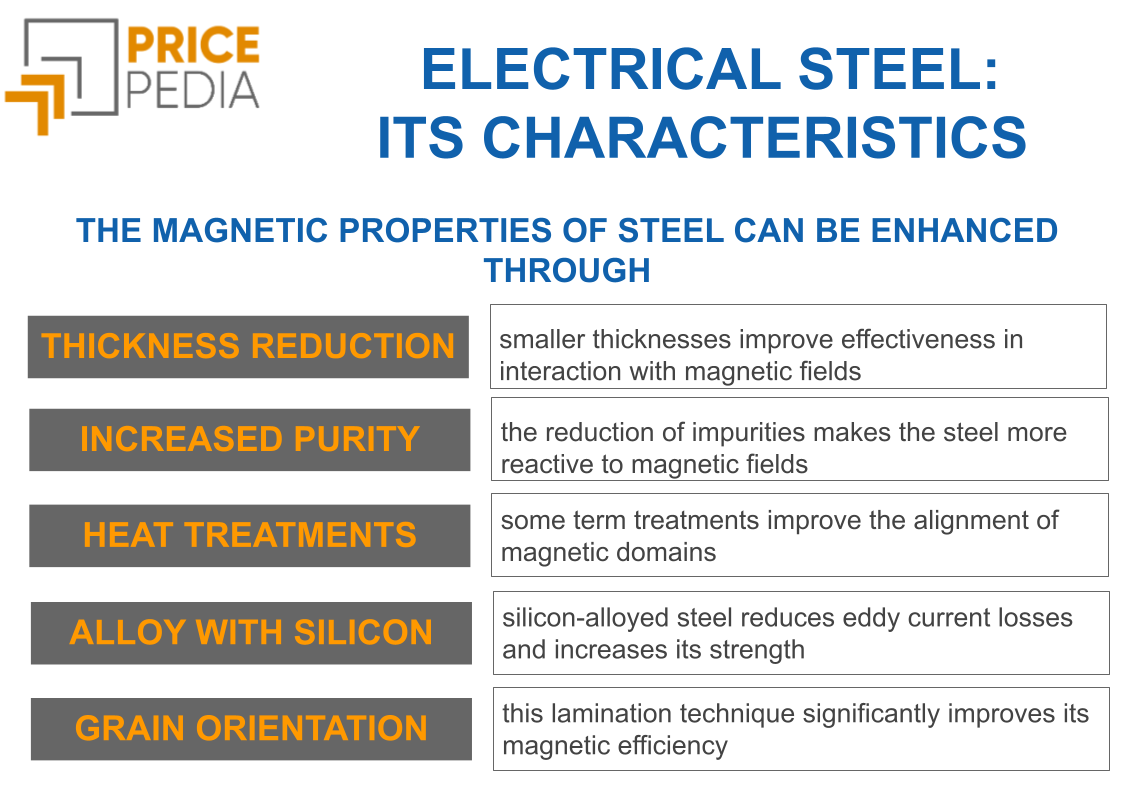
[1] Steel is generally magnetically responsive. However, its magnetic properties can be enhanced through:
- Reducing the material's thickness: Thinner material can offer greater surface magnetic saturation, improving interaction with magnetic fields.
- Improving purity: Removing impurities such as sulfur, phosphorus, and oxygen can enhance the magnetic permeability of iron or steel, making them more responsive to magnetic fields;
- Through heat treatments: Heat treatments can alter the microscopic structure of iron or steel, reducing internal stresses and improving the alignment of magnetic domains, which enhances magnetic properties;
- Alloying with other materials: Elements such as silicon, nickel, cobalt, and aluminum can be added to form alloys with better magnetic properties. Silicon, in particular, is widely used to reduce eddy current losses and increase the electrical resistance of steel;
- Laminating with grain orientation: This lamination technique optimizes the alignment of iron crystals within the steel, significantly improving its magnetic efficiency, especially in electromagnetic applications like transformers and electric motors.
Methods to increase the magnetic properties of steel