Monetary policy and commodity prices
Economic theory highlights how a reduction in interest rates leads to an increase in commodity prices
Published by Pasquale Marzano. .
Real Prices Monetary Policy Price Drivers
The continuation of the weakness phase of the global economic cycle, particularly in manufacturing, and the slowdown in inflation have intensified the debate in recent weeks on when the restrictive monetary policy implemented by the World's major Central Banks will be eased.
Market participants expect a first reduction in interest rates to plausibly occur in June 2024, barring unforeseen inflation shocks, as also indicated in the weekly update The "stop and go" of commodity prices continues.
The reduction in rates would lead to lower cost of money, which should incentivize investments and give a greater push to energy and digital transition, favoring the demand for commodities and, consequently, a possible new expansionary cycle of commodity prices, after the reduction phase since summer 2022 (as shown in the graph).
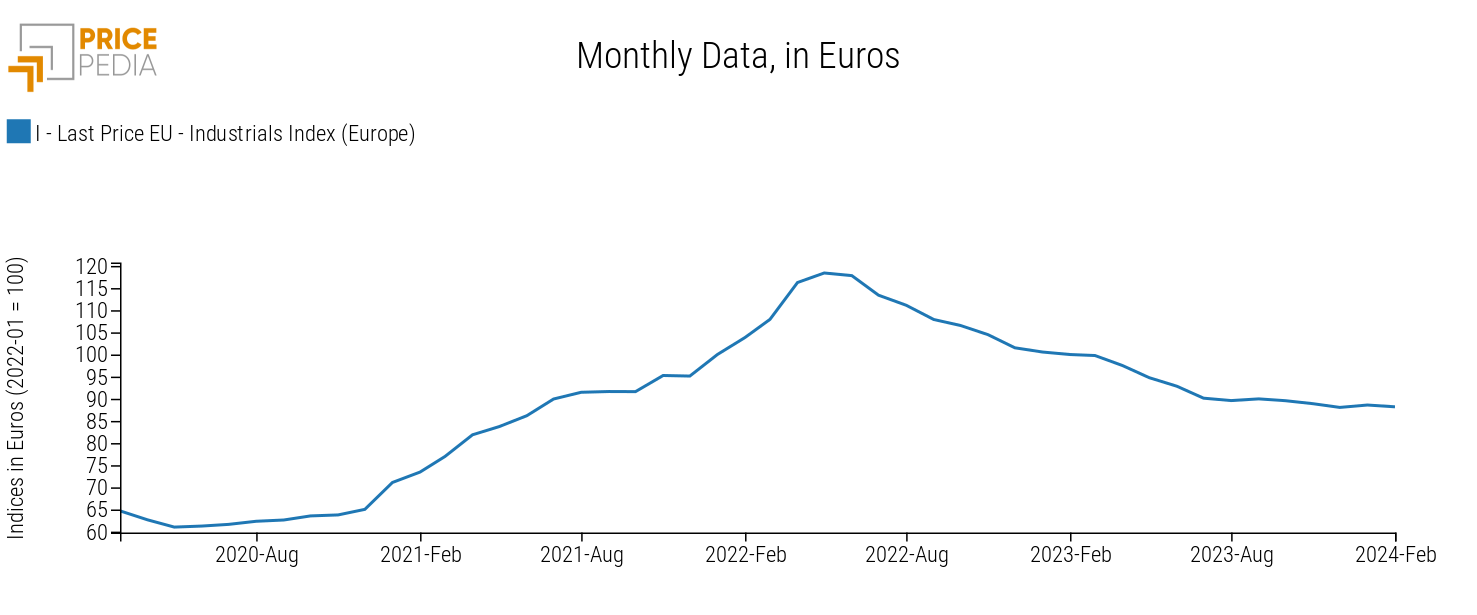
Relationship between Monetary Policy and Commodity Prices
In general, economic theory has repeatedly studied the relationship between monetary policy and commodity prices. This relationship is inverse: as interest rates increase/decrease, commodity prices decrease/increase.
In general, the channels through which monetary policy affects commodity prices are[1]:
- Cost of carry: Interest rate variations influence the opportunity cost of storing commodities. Consequently, a substantial reduction in interest rates provides investors with an incentive to increase commodity inventories;
- Real economy: Reduction in interest rates affects investments and consumption, which in turn drives current and future consumption of commodities. Although the real effects of monetary policy take time to materialize, investors in commodity markets adjust their portfolios today in anticipation of future changes. Therefore, since various commodities, such as base metals, are heavily exposed to investment demand, industrial commodity prices are expected to react to monetary policy shocks;
- Liquidity: The monetary policy of major central banks affects global financial conditions and, therefore, guides liquidity in physical and derivative markets.
The relationship between interest rates and commodity prices, whose importance is emphasized by economic theory, is also confirmed by data.
A preliminary estimate of this relationship, obtained by regressing the index of industrial commodity prices in real-term against the real-term price of oil, the industrial cycle, and changes in real interest rates, produces a negative and significant coefficient of interest rates, confirming how their variation determines opposite changes in commodity prices.
Do you want to stay up-to-date on commodity market trends?
Sign up for PricePedia newsletter: it's free!
Conclusions
Economic theory and empirical evidence from previous commodity price cycles suggest a possible new phase of price increases in relation to the expected reduction in rates to begin next summer.
The reduction in rates is expected to occur very gradually. Therefore, the effects on commodity prices will be, at least initially, weak.
1. See the International Monetary Fund paper Monetary Policy Transmission through Commodity Prices Pasquale Marzano
Economist and data scientist. At PricePedia he deals with the analysis of commodity markets, forecasting models for raw material prices and management of reference databases.