Polyols for Polyurethanes: The Strategic Role of the Chinese Industry
Interdependencies Between Regional Markets and Related Products
Published by Luigi Bidoia. .
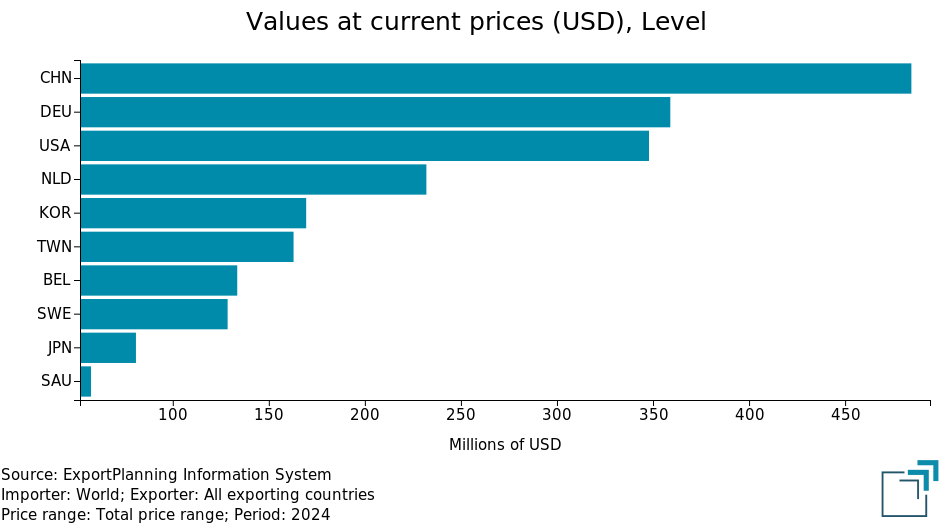
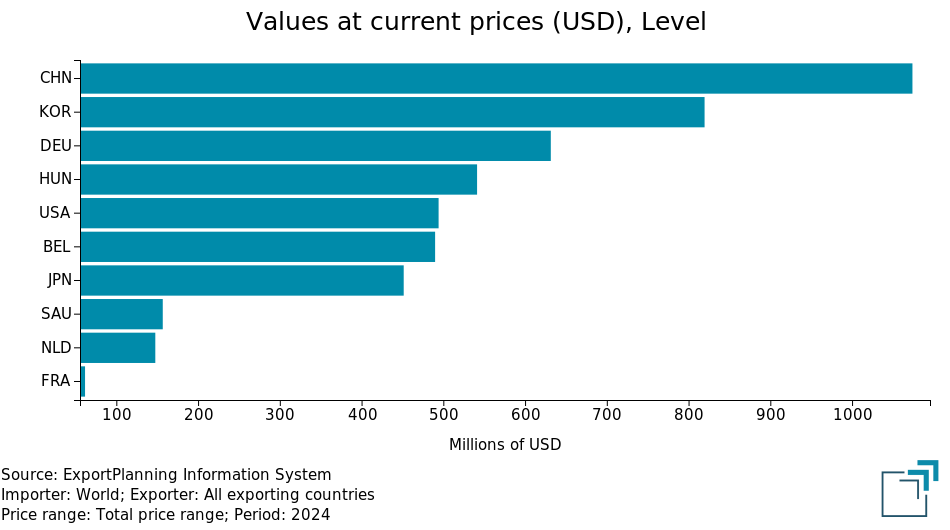
Polyurethanes Chinese industryWithin the polyurethane supply chain, China holds a leading position in both the production and consumption of the two essential raw materials: polyols and isocyanates. This leadership is also reflected in international trade, where China stands as the world's largest exporter of these chemical commodities, as shown in the figures below.
Top 10 exporters in 2024
| Polyols for polyurethanes | Isocyanates |
|
|
In the polyols market, China’s dominance is challenged mainly by Germany and the United States. In the case of isocyanates, Germany remains among the top three global exporters, while South Korea takes the place of the United States on the podium.
The article Price cycles of isocyanates highlighted that:
- Cost factors play a less central role in price formation compared with supply–demand dynamics.
- The prices of different types of isocyanates are strongly correlated, suggesting that common market drivers—such as relative availability, stock management strategies, and substitution possibilities—exert a predominant influence compared to cost dynamics.
This article focuses on polyols for polyurethanes, in particular 1,4 Butanediol and Trimethylolpropane. Their market behavior shows strong similarities to that of isocyanates:
- Limited impact of cost factors on price trends.
- Strong correlation between the prices of the two polyols.
Polyols and Polyols for Polyurethanes
Polyols (also known as polyalcohols or glycols) are a broad family of organic compounds characterized by the presence of multiple hydroxyl –OH groups. Although they share the same basic chemical function, their applications vary widely depending on molecular structure, purity, and the physical properties required in different end uses. From a market perspective, three main categories of polyols can be identified:
- Food-grade polyols (such as sorbitol, mannitol, xylitol), used as sweeteners in foods, chewing gum, bakery products, and pharmaceuticals.
- Industrial polyols not intended for polyurethane production, employed in the manufacture of resins, lubricants, inks, solvents, antifreeze, and cosmetics.
- Industrial polyols specifically used in the production of polyurethanes.
Do you want to stay up-to-date on commodity market trends?
Sign up for PricePedia newsletter: it's free!
Polyols for Polyurethanes
Industrial polyols for polyurethanes represent one of the two fundamental chemical pillars of polyurethane chemistry, alongside isocyanates. The main commodities in this category include polyether polyols, polyester polyols, 1,4-butanediol (BDO), and trimethylolpropane (TMP). These polyols define the mechanical, elastic, and structural properties of polyurethane materials across their many applications. The analysis below focuses on the market behavior of BDO and TMP.
Limited Impact of Costs on Prices
The markets for BDO and TMP show strong resilience to fluctuations in raw material costs.
For 1,4-butanediol (BDO), the availability of multiple production pathways—each relying on different feedstocks—dampens the influence of upstream cost swings on the product’s final market price.
Similarly, although the most common industrial process for producing trimethylolpropane (TMP) is based on the reaction between n-butyraldehyde and formaldehyde in an alkaline environment, several process variations and alternative feedstock sources exist. This makes TMP, like BDO, a product that can be manufactured from multiple raw materials.
When several viable production routes are available, cost increases that affect only part of the supply chain tend to translate primarily into margin erosion for those specific processes, rather than into significant changes in the market prices of BDO and TMP.
Correlation Between the Prices of 1,4-Butanediol and Trimethylolpropane
The most distinctive factor in the price formation of the two products is the strong correlation observed between BDO and TMP prices, both in the Chinese market and, even more markedly, in the European market. The figure below shows the simple correlations among the four prices considered: the FOB export prices of BDO and TMP from China and the corresponding intra-EU customs values.
Simple correlations between polyol prices in the European and Chinese markets
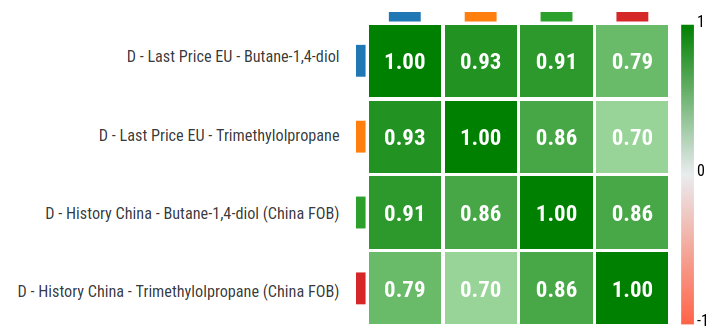
The simple correlation between European prices of BDO and TMP is 0.93, indicating a strong alignment in their price movements. The correlation between the Chinese FOB prices of the two products is also high (0.86), confirming a similar joint dynamic in the Chinese market.
The connection between European and Chinese markets is particularly strong for BDO (0.91), while the relationship between European and Chinese prices of TMP appears, at first glance, relatively weaker — a relationship that, however, becomes clearer when considering a delay of 4–5 months with which the European market reacts to changes in the Chinese market.
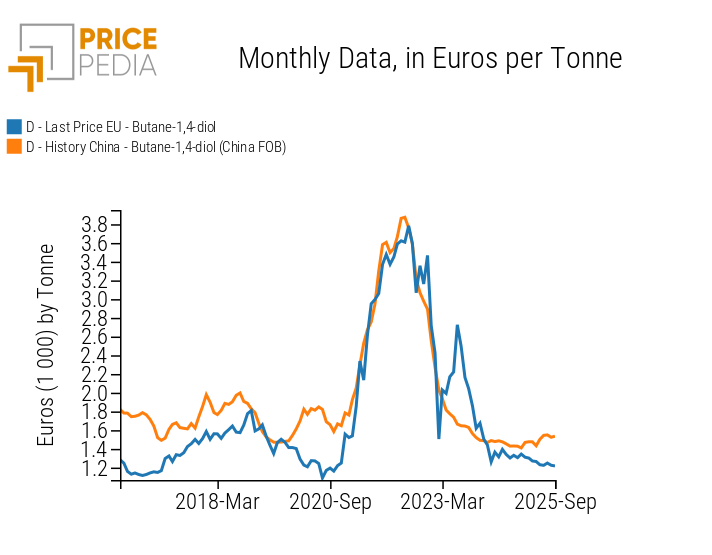
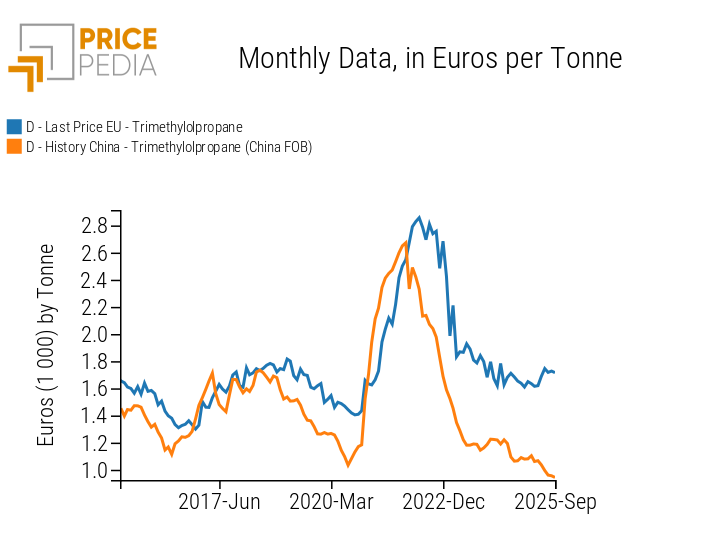
These dynamics emerge more clearly from the graphs below: the first compares BDO prices in Europe and China, while the second shows the same comparison for TMP.
Comparison between European and Chinese prices
| 1,4-Butanediol | Trimethylolpropane |
|
|
The comparison between European and Chinese prices of 1,4-Butanediol highlights the strong link binding the two markets. This connection is not perfect, however: there are periods where the two price trends diverge significantly. A notable example is spring 2023, when the European price of BDO surged from €1,500 to €2,700 per tonne in just six months, while the Chinese price continued its downward trajectory.
The relationship between European and Chinese markets for Trimethylolpropane is also significant, particularly when accounting for the 4–5 month lag with which the European price tends to respond to developments in the Chinese market.
Summary
Polyols for polyurethanes represent a specific subcategory of polyols and, together with isocyanates, play a crucial role in polyurethane production.
Both polyurethane polyols and isocyanates share several key market characteristics: price formation that is only weakly influenced by cost fluctuations, strong correlations between the prices of products within the same family in a given regional market, and equally strong connections between the prices of the same commodity in the European and Asian markets.
The result is a tightly interconnected system of markets that influence one another and can only be properly understood through an integrated analytical approach. Examining, for example, the drivers of the European price of 1,4-Butanediol in isolation would not be sufficient to explain its movements. Only a combined and comparative analysis of all four price series allows us to identify the market forces that, over time, contribute to shaping each individual price.

