PricePedia Scenario for January 2026
Weak demand and downward pressures characterize input material prices in 2026-2027
Published by Pasquale Marzano. .
Forecast ForecastThe PricePedia Scenario, updated with information available as of January 8, 2026, outlines an overall downward-oriented outlook for raw material prices over the 2026-2027 period. Weak global commodity demand is expected to continue exerting negative pressure on input material prices.
From a macroeconomic perspective, while the slowdown in the global economic cycle in 2025 proved less severe than initially expected, increasing economic fragmentation and the effects of tighter trade policies are expected to weigh more visibly on commodity demand in the coming months, particularly in 2026.
In this context, global industrial production, representative of commodity demand, is expected to expand at subdued rates in 2026, before showing a more sustained recovery in 2027.
The trajectory of the global industrial cycle[1], developed by PricePedia and shown below, reflects this pattern.
Global industrial cycle, January 2026 scenario
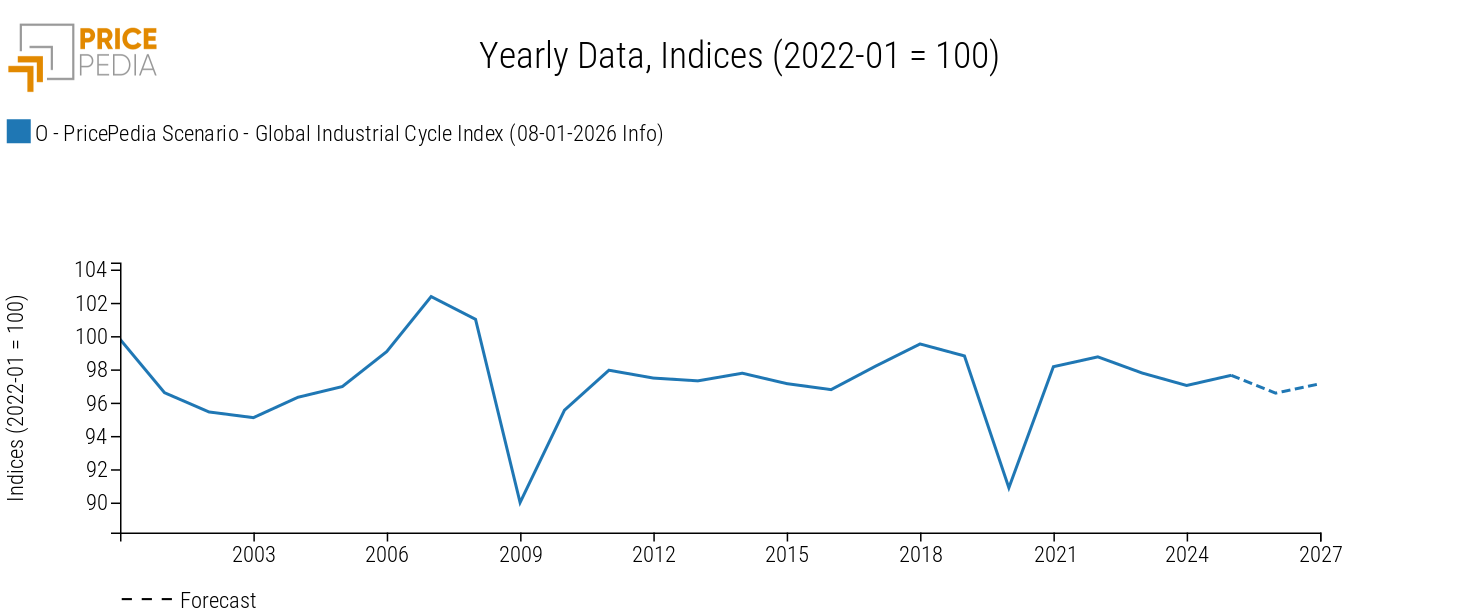
In 2026, the global industrial cycle is expected to contract by more than -1%. This implies modest growth in commodity demand, insufficient to generate significant market tensions, particularly in the current context of excess supply.
In 2027, the global industrial cycle is expected to post a moderate recovery, with growth of +0.6%.
The price outlook for input materials
Against a backdrop of weak global demand, the outlook for raw material prices remains predominantly downward-oriented.
Consistent with the expected evolution of the global industrial cycle, raw material prices are projected to decline by an average of -7% in 2026 compared to 2025 average levels. In 2027, prices are expected to stabilize, remaining approximately -0.6% below the previous year’s average.
The expected price dynamics are summarized in the table below, which reports annual percentage changes in euro terms for the main commodity aggregates included in the PricePedia Scenario: Industrials[2], Commodity[3], Energy, and Food.
Table 1: Annual rates of change (%) of the PricePedia Aggregate Indices, in Euro
| 2024 | 2025 | 2026f | 2027f | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I-PricePedia Scenario-Commodity Index (Europe) (08-01-2026 Info) | −4.59 | −5.98 | −7.01 | −0.64 |
| I-PricePedia Scenario-Energy Total Index (Europe) (08-01-2026 Info) | −5.89 | −12.35 | −14.91 | −2.92 |
| I-PricePedia Scenario-Industrials Index (Europe) (08-01-2026 Info) | −4.58 | −2.92 | +0.65 | +2.29 |
| I-PricePedia Scenario-Food Total Index (Europe) (08-01-2026 Info) | +2.33 | +9.90 | −5.19 | −1.97 |
Energy commodities are expected to experience the strongest downward pressures. Following the -12% contraction recorded in 2025, prices are projected to decline by a further -15% in 2026. Despite the sector’s continued exposure to geopolitical uncertainties, not least those related to developments in Venezuela and Iran, energy markets remain characterized by a persistent oversupply.
Food commodity prices are also expected to decline in 2026, by -5.2% compared to the elevated levels recorded last year. This decrease mainly reflects a normalization phase following the sharp increases observed previously, amid overall less constrained supply conditions. The downward trend is expected to continue into 2027, with prices declining by around -2% relative to the 2026 average.
With regard to industrial commodities, the outlook appears more heterogeneous. On aggregate, prices are expected to increase modestly by +0.6% in 2026, following the nearly -3% decline recorded in 2025. Price support is driven primarily by industrial metals linked to energy and digital transition processes, whose demand prospects continue to benefit from expectations of structurally higher long-term usage.
1. The global industrial cycle index is constructed by purifying the actual dynamics of industrial production from its trend. Since the supply of commodities tends to vary according to long-term economic growth expectations, while the demand for commodities is more linked to actual cyclical uses, the global industrial cycle index tends to reproduce the conditions of tension between demand and supply on the commodity market: when it increases, it means that the demand for commodities increases more than the supply; vice versa when it decreases.
2. The PricePedia Industrials index results from the aggregation of the indices relating to the following product categories: Ferrous, Non-Ferrous, Wood and Paper, Chemicals: Specialty, Organic Chemicals, Inorganic Chemicals, Plastics and Elastomers and Textile Fibres.
3. The PricePedia Commodity index results from the aggregation of the indices relating to industrial, food and energy commodities.


